Exploring Ubuntu Package Management: A Comprehensive Guide
The Ultimate Guide to Ubuntu Package Management
Are you an Ubuntu user looking to maximize the potential of your system through effective package management? Ubuntu, known for its user-friendly interface and robust functionalities, offers a diverse range of package management tools to streamline software installations, updates, and removals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of Ubuntu package management, exploring tips, tricks, and best practices to enhance your user experience.
Understanding Package Management in Ubuntu
Package management lies at the core of every Linux distribution, including Ubuntu. Packages are software bundles that contain applications, libraries, dependencies, and configuration files necessary for smooth program execution. Ubuntu’s package management system revolves around the Advanced Package Tool (APT), a powerful command-line tool that simplifies the process of installing, upgrading, and removing software packages.
Installing Packages with APT
One of the most common tasks in Ubuntu package management is installing new software packages. With APT, you can easily install packages from the official Ubuntu repositories as well as third-party repositories. To install a package, simply use the following command:
sudo apt-get install package_name
Replace ‘package_name’ with the name of the package you wish to install. APT will automatically resolve dependencies and download the necessary files from the repository.
Managing Repositories
Ubuntu repositories are collections of software packages maintained by Ubuntu developers or third-party contributors. By managing repositories effectively, you can access a vast array of software applications tailored to your needs. To add a new repository to your system, use the ‘add-apt-repository’ command:
sudo add-apt-repository repository_url
Replace ‘repository_url’ with the URL of the repository you want to add. This allows you to install software packages from the newly added repository using APT.
Updating and Upgrading Packages
Regularly updating and upgrading packages is crucial to ensure system stability and security. To update the package list and upgrade installed packages, use the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
APT will fetch the latest package information from the repositories and upgrade the installed packages to their latest versions.
Removing Packages
When you no longer need a software package, you can easily remove it from your system using APT. The following command allows you to remove a package without deleting its configuration files:
sudo apt-get remove package_name
For a complete removal, including configuration files, use:
sudo apt-get purge package_name
Conclusion
Package management is a fundamental aspect of Ubuntu system administration, enabling users to customize their systems with a myriad of software options. By mastering the tools and techniques outlined in this guide, you can optimize your Ubuntu experience and harness the full potential of your operating system.
-
 01
01Further Discussion About Protein Bar Packing Machinery
27-02-2024 -
 02
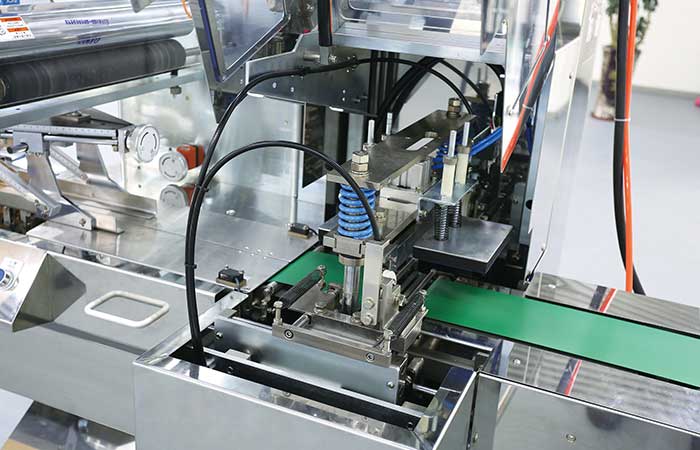
02Sustain The Best Crispy With Automatic Packaging Machines
29-01-2024 -
 03
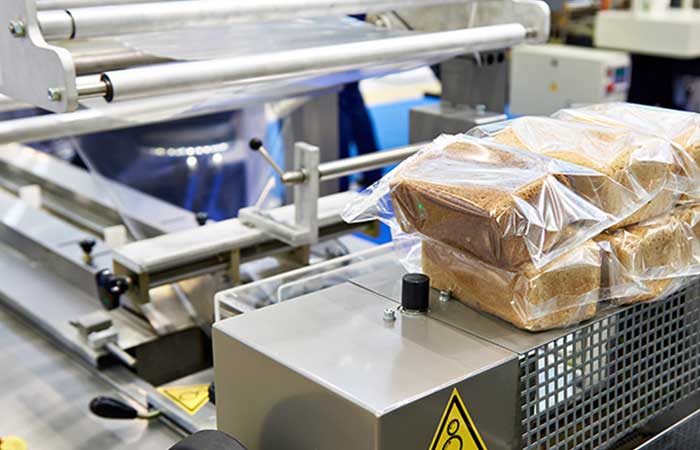
03Bread Packing Machine For Bakery Business
19-01-2024 -
 04
04How Flow Wrappers Are Adapting to Changing Trends
01-11-2023 -
 05
05The Comprehensive Guide to Packaging Machinery
31-10-2023 -
 06
06Automatic Cookie Packaging System Performance
01-09-2023 -
 07
07Streamlining Biscuit Packaging with Multipack Biscuit Packaging Machines
25-08-2023 -
 08
08From Assembly To Shipping: The Energy Bar Packaging Machine Does All
28-02-2023 -
 09
09Maximizing Efficiency With Food Packaging Machine Technology
22-02-2023 -
 10
10Clients Hunt For Professional And Functional Packaging Machine
10-11-2022